Database scheme
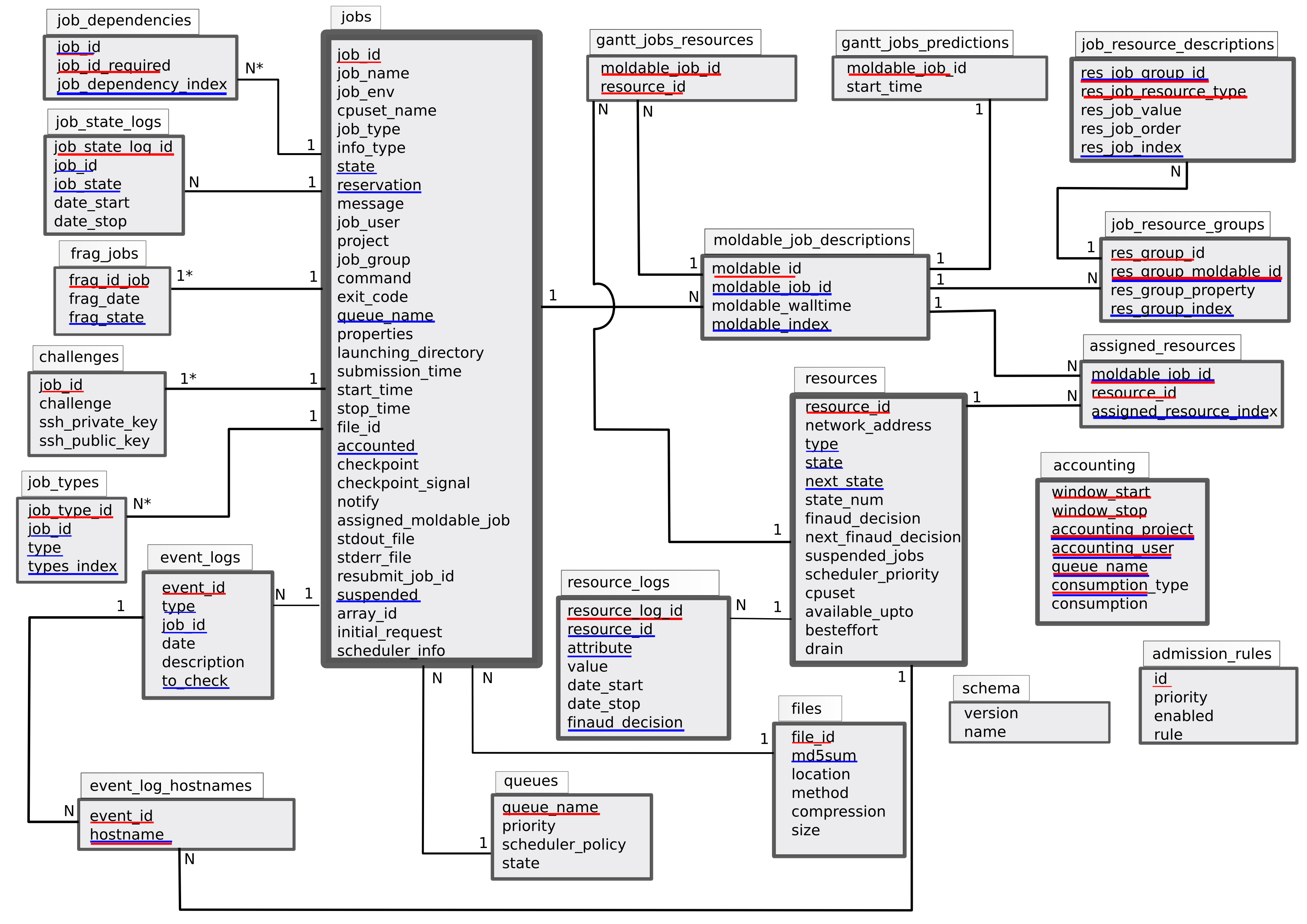
Database scheme (red lines seem PRIMARY KEY, blue lines seem INDEX)
Note : all dates and duration are stored in an integer manner (number of seconds since the EPOCH).
accounting
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
window_start |
INT UNSIGNED |
start date of the accounting interval |
window_stop |
INT UNSIGNED |
stop date of the accounting interval |
accounting_user |
VARCHAR(20) |
user name |
accounting_project |
VARCHAR(255) |
name of the related project |
queue_name |
VARCHAR(100) |
queue name |
consumption_type |
ENUM(“ASKED”, “USED”) |
“ASKED” corresponds to the walltimes specified by the user. “USED” corresponds to the effective time used by the user. |
consumption |
INT UNSIGNED |
number of seconds used |
- Primary key
window_start, window_stop, accounting_user, queue_name, accounting_project, consumption_type
- Index fields
window_start, window_stop, accounting_user, queue_name, accounting_project, consumption_type
This table is a summary of the consumption for each user on each queue. This increases the speed of queries about user consumptions and statistic generation.
Data are inserted through the command oaraccounting (when a job is treated the field accounted in table jobs is passed into “YES”). So it is possible to regenerate this table completely in this way :
Delete all data of the table:
DELETE FROM accounting;Set the field accounted in the table jobs to “NO” for each row:
UPDATE jobs SET accounted = "NO";Run the oaraccounting command.
You can change the amount of time for each window : edit the oar configuration file and change the value of the tag ACCOUNTING_WINDOW.
schema
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
version |
VARCHAR(255) |
database schema version number |
name |
VARCHAR(255) |
optional name |
This table is used to store the version of the database schema.
So the oar-database command be used to automatically upgrade the schema from any version with:
oar-database --setup
admission_rules
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
id |
INT UNSIGNED |
id number |
rule |
TEXT |
rule written in Perl applied when a job is going to be registered |
- Primary key
id
- Index fields
None
You can use these rules to change some values of some properties when a job is submitted. So each admission rule is executed in the order of the id field and it can set several variables. If one of them exits then the others will not be evaluated and oarsub returns an error.
The rules can be added with the following command:
oaradmissionrules -n
Some examples are better than a long description:
Specify the default value for queue parameter
if (not defined($queue_name)) { $queue_name="default"; }Avoid users except oar to go in the admin queue
if (($queue_name eq "admin") && ($user ne "oar")) { die("[ADMISSION RULE] Only oar user can submit jobs in the admin queue\n"); }Restrict the maximum of the walltime for interactive jobs
my $max_walltime = OAR::IO::sql_to_duration("12:00:00"); if ($jobType eq "INTERACTIVE"){ foreach my $mold (@{$ref_resource_list}){ if ( (defined($mold->[1])) and ($max_walltime < $mold->[1]) ){ print("[ADMISSION RULE] Walltime to big for an INTERACTIVE job so it is set to $max_walltime.\n"); $mold->[1] = $max_walltime; } } }Specify the default walltime
my $default_wall = OAR::IO::sql_to_duration("2:00:00"); foreach my $mold (@{$ref_resource_list}){ if (!defined($mold->[1])){ print("[ADMISSION RULE] Set default walltime to $default_wall.\n"); $mold->[1] = $default_wall; } }How to perform actions if the user name is in a file
open(FILE, "/tmp/users.txt"); while (($queue_name ne "admin") and ($_ = <FILE>)){ if ($_ =~ m/^\\s*$user\\s*$/m){ print("[ADMISSION RULE] Change assigned queue into admin\n"); $queue_name = "admin"; } } close(FILE);How to automatically add a job type depending of the walltime and an estimation of the number of resources of the job
foreach my $e (estimate_job_nb_resources($dbh_ro, $ref_resource_list, $jobproperties)){ #print("AREA: $e->{nbresources} x $e->{walltime} = ".$e->{nbresources} * $e->{walltime}."\n"); if ($e->{nbresources} * $e->{walltime} > 24*3600*1){ print("[ADMISSION RULE] Your job is of the 'big' type\n"); push(@{$type_list},"big"); last; } }
You can print all the admission rules with:
oaradmissionrules -S -f
event_logs
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
event_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
event identifier |
type |
VARCHAR(50) |
event type |
job_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
job related of the event |
date |
INT UNSIGNED |
event date |
description |
VARCHAR(255) |
textual description of the event |
to_check |
ENUM(‘YES’, ‘NO’) |
specify if the module NodeChangeState must check this event to Suspect or not some nodes |
- Primary key
event_id
- Index fields
type, to_check
The different event types are:
“PING_CHECKER_NODE_SUSPECTED” : the system detected via the module “finaud” that a node is not responding.
“PROLOGUE_ERROR” : an error occurred during the execution of the job prologue (exit code != 0).
“EPILOGUE_ERROR” : an error occurred during the execution of the job epilogue (exit code != 0).
“CANNOT_CREATE_TMP_DIRECTORY” : OAR cannot create the directory where all information files will be stored.
“CAN_NOT_WRITE_NODE_FILE” : the system was not able to write file which had to contain the node list on the first node (/tmp/OAR_job_id).
“CAN_NOT_WRITE_PID_FILE” : the system was not able to write the file which had to contain the pid of oarexec process on the first node (/tmp/pid_of_oarexec_for_job_id).
“USER_SHELL” : the system was not able to get informations about the user shell on the first node.
“EXIT_VALUE_OAREXEC” : the oarexec process terminated with an unknown exit code.
“SEND_KILL_JOB” : signal that OAR has transmitted a kill signal to the oarexec of the specified job.
“LEON_KILL_BIPBIP_TIMEOUT” : Leon module has detected that something wrong occurred during the kill of a job and so kill the local bipbip process.
“EXTERMINATE_JOB” : Leon module has detected that something wrong occurred during the kill of a job and so clean the database and terminate the job artificially.
“WORKING_DIRECTORY” : the directory from which the job was submitted does not exist on the node assigned by the system.
“OUTPUT_FILES” : OAR cannot write the output files (stdout and stderr) in the working directory.
“CANNOT_NOTIFY_OARSUB” : OAR cannot notify the oarsub process for an interactive job (maybe the user has killed this process).
“WALLTIME” : the job has reached its walltime.
“SCHEDULER_REDUCE_NB_NODES_FOR_RESERVATION” : this means that there is not enough nodes for the reservation and so the scheduler do the best and gives less nodes than the user wanted (this occurres when nodes become Suspected or Absent).
“BESTEFFORT_KILL” : the job is of the type besteffort and was killed because a normal job wanted the nodes.
“FRAG_JOB_REQUEST” : someone wants to delete a job.
“CHECKPOINT” : the checkpoint signal was sent to the job.
“CHECKPOINT_ERROR” : OAR cannot send the signal to the job.
“CHECKPOINT_SUCCESS” : system has sent the signal correctly.
“SERVER_EPILOGUE_TIMEOUT” : epilogue server script has time outed.
“SERVER_EPILOGUE_EXIT_CODE_ERROR” : epilogue server script did not return 0.
“SERVER_EPILOGUE_ERROR” : cannot find epilogue server script file.
“SERVER_PROLOGUE_TIMEOUT” : prologue server script has time outed.
“SERVER_PROLOGUE_EXIT_CODE_ERROR” : prologue server script did not return 0.
“SERVER_PROLOGUE_ERROR” : cannot find prologue server script file.
“CPUSET_CLEAN_ERROR” : OAR cannot clean correctly cpuset files for a job on the remote node.
“MAIL_NOTIFICATION_ERROR” : a mail cannot be sent.
“USER_MAIL_NOTIFICATION” : user mail notification cannot be performed.
“USER_EXEC_NOTIFICATION_ERROR” : user script execution notification cannot be performed.
“BIPBIP_BAD_JOBID” : error when retrieving informations about a running job.
“BIPBIP_CHALLENGE” : OAR is configured to detach jobs when they are launched on compute nodes and the job return a bad challenge number.
“RESUBMIT_JOB_AUTOMATICALLY” : the job was automatically resubmitted.
“WALLTIME” : the job reached its walltime.
“REDUCE_RESERVATION_WALLTIME” : the reservation job was shrunk.
“SSH_TRANSFER_TIMEOUT” : node OAR part script was too long to transfer.
“BAD_HASHTABLE_DUMP” : OAR transfered a bad hashtable.
“LAUNCHING_OAREXEC_TIMEOUT” : oarexec was too long to initialize itself.
“RESERVATION_NO_NODE” : All nodes were detected as bad for the reservation job.
event_log_hostnames
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
event_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
event identifier |
hostname |
VARCHAR(255) |
name of the node where the event has occured |
- Primary key
event_id
- Index fields
hostname
This table stores hostnames related to events like “PING_CHECKER_NODE_SUSPECTED”.
files
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
idFile |
INT UNSIGNED |
|
md5sum |
VARCHAR(255) |
|
location |
VARCHAR(255) |
|
method |
VARCHAR(255) |
|
compression |
VARCHAR(255) |
|
size |
INT UNSIGNED |
- Primary key
idFile
- Index fields
md5sum
frag_jobs
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
frag_id_job |
INT UNSIGNED |
job id |
frag_date |
INT UNSIGNED |
kill job decision date |
frag_state |
ENUM(‘LEON’, ‘TIMER_ARMED’ , ‘LEON_EXTERMINATE’, ‘FRAGGED’) DEFAULT ‘LEON’ |
state to tell Leon what to do |
- Primary key
frag_id_job
- Index fields
frag_state
What do these states mean:
“LEON” : the Leon module must try to kill the job and change the state into “TIMER_ARMED”.
“TIMER_ARMED” : the Sarko module must wait a response from the job during a timeout (default is 60s)
“LEON_EXTERMINATE” : the Sarko module has decided that the job time outed and asked Leon to clean up the database.
“FRAGGED” : job is fragged.
gantt_jobs_resources
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
moldable_job_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
moldable job id |
resource_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
resource assigned to the job |
- Primary key
moldable_job_id, resource_id
- Index fields
None
This table specifies which resources are attributed to which jobs.
gantt_jobs_resources_visu
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
moldable_job_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
moldable job id |
resource_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
resource assigned to the job |
- Primary key
moldable_job_id, resource_id
- Index fields
None
This table is the same as gantt_jobs_resources and is used by visualisation tools. It is updated atomically (a lock is used).
gantt_jobs_predictions
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
moldable_job_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
job id |
start_time |
INT UNSIGNED |
date when the job is scheduled to start |
- Primary key
moldable_job_id
- Index fields
None
With this table and gantt_jobs_resources you can know exactly what are the decisions taken by the schedulers for each waiting jobs.
- note
The special job id “0” is used to store the scheduling reference date.
gantt_jobs_predictions_visu
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
moldable_job_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
job id |
start_time |
INT UNSIGNED |
date when the job is scheduled to start |
- Primary key
job_id
- Index fields
None
This table is the same as gantt_jobs_predictions and is used by visualisation tools. It is made up to date in an atomic action (with a lock).
jobs
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
job_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
job identifier |
array_id |
INT |
array identifier |
array_index |
INT |
index of the job in the array |
initial_request |
TEXT |
oarsub initial arguments |
job_name |
VARCHAR(100) |
name given by the user |
cpuset_name |
VARCHAR(255) |
name of the cpuset directory used for this job on each nodes |
job_type |
ENUM(‘INTERACTIVE’, ‘PASSIVE’) DEFAULT ‘PASSIVE’ |
specify if the user wants to launch a program or get an interactive shell |
info_type |
VARCHAR(255) |
some informations about oarsub command |
state |
ENUM(‘Waiting’,’Hold’, ‘toLaunch’, ‘toError’, ‘toAckReservation’, ‘Launching’, ‘Running’ ‘Suspended’, ‘Resuming’, , ‘Finishing’, ‘Terminated’, ‘Error’) |
job state |
reservation |
ENUM(‘None’, ‘toSchedule’, ‘Scheduled’) DEFAULT ‘None’ |
specify if the job is a reservation and the state of this one |
message |
VARCHAR(255) |
readable information message for the user |
job_user |
VARCHAR(255) |
user name |
command |
TEXT |
program to run |
queue_name |
VARCHAR(100) |
queue name |
properties |
TEXT |
properties that assigned nodes must match |
launching_directory |
TEXT |
path of the directory where to launch the user process |
submission_time |
INT UNSIGNED |
date when the job was submitted |
start_time |
INT UNSIGNED |
date when the job was launched |
stop_time |
INT UNSIGNED |
date when the job was stopped |
file_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
|
accounted |
ENUM(“YES”, “NO”) DEFAULT “NO” |
specify if the job was considered by the accounting mechanism or not |
notify |
VARCHAR(255) |
gives the way to notify the user about the job (mail or script ) |
assigned_moldable_job |
INT UNSIGNED |
moldable job chosen by the scheduler |
checkpoint |
INT UNSIGNED |
number of seconds before the walltime to send the checkpoint signal to the job |
checkpoint_signal |
INT UNSIGNED |
signal to use when checkpointing the job |
stdout_file |
TEXT |
file name where to redirect program STDOUT |
stderr_file |
TEXT |
file name where to redirect program STDERR |
resubmit_job_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
if a job is resubmitted then the new one store the previous |
project |
VARCHAR(255) |
arbitrary name given by the user or an admission rule |
suspended |
ENUM(“YES”,”NO”) |
specify if the job was suspended (oarhold) |
job_env |
TEXT |
environment variables to set for the job |
exit_code |
INT DEFAULT 0 |
exit code for passive jobs |
job_group |
VARCHAR(255) |
not used |
- Primary key
job_id
- Index fields
state, reservation, queue_name, accounted, suspended
Explications about the “state” field:
“Waiting” : the job is waiting OAR scheduler decision.
“Hold” : user or administrator wants to hold the job (oarhold command). So it will not be scheduled by the system.
“toLaunch” : the OAR scheduler has attributed some nodes to the job. So it will be launched.
“toError” : something wrong occurred and the job is going into the error state.
“toAckReservation” : the OAR scheduler must say “YES” or “NO” to the waiting oarsub command because it requested a reservation.
“Launching” : OAR has launched the job and will execute the user command on the first node.
“Running” : the user command is executing on the first node.
“Suspended” : the job was in Running state and there was a request (oarhold with “-r” option) to suspend this job. In this state other jobs can be scheduled on the same resources (these resources has the “suspended_jobs” field to “YES”).
“Finishing” : the user command has terminated and OAR is doing work internally
“Terminated” : the job has terminated normally.
“Error” : a problem has occurred.
Explications about the “reservation” field:
“None” : the job is not a reservation.
“toSchedule” : the job is a reservation and must be approved by the scheduler.
“Scheduled” : the job is a reservation and is scheduled by OAR.
job_dependencies
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
job_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
job identifier |
job_id_required |
INT UNSIGNED |
job needed to be completed before launching job_id |
- Primary key
job_id, job_id_required
- Index fields
job_id, job_id_required
This table is feeded by oarsub command with the “-a” option.
moldable_job_descriptions
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
moldable_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
moldable job identifier |
moldable_job_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
corresponding job identifier |
moldable_walltime |
INT UNSIGNED |
instance duration |
- Primary key
moldable_id
- Index fields
moldable_job_id
A job can be described with several instances. Thus OAR scheduler can choose one of them. For example it can calculate which instance will finish first. So this table stores all instances for all jobs.
job_resource_groups
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
res_group_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
group identifier |
res_group_moldable_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
corresponding moldable job identifier |
res_group_property |
TEXT |
SQL constraint properties |
- Primary key
res_group_id
- Index fields
res_group_moldable_id
As you can specify job global properties with oarsub and the “-p” option, you can do the same thing for each resource groups that you define with the “-l” option.
job_resource_descriptions
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
res_job_group_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
corresponding group identifier |
res_job_resource_type |
VARCHAR(255) |
resource type (name of a field in resources) |
res_job_value |
INT |
wanted resource number |
res_job_order |
INT UNSIGNED |
order of the request |
- Primary key
res_job_group_id, res_job_resource_type, res_job_order
- Index fields
res_job_group_id
This table store the hierarchical resource description given with oarsub and the “-l” option.
job_state_logs
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
job_state_log_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
identifier |
job_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
corresponding job identifier |
job_state |
ENUM(‘Waiting’, ‘Hold’, ‘toLaunch’, ‘toError’, ‘toAckReservation’, ‘Launching’, ‘Finishing’, ‘Running’, ‘Suspended’, ‘Resuming’, ‘Terminated’, ‘Error’) |
job state during the interval |
date_start |
INT UNSIGNED |
start date of the interval |
date_stop |
INT UNSIGNED |
end date of the interval |
- Primary key
job_state_log_id
- Index fields
job_id, job_state
This table keeps informations about state changes of jobs.
job_types
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
job_type_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
identifier |
job_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
corresponding job identifier |
type |
VARCHAR(255) |
job type like “deploy”, “timesharing”, … |
type_index |
ENUM(‘CURRENT’, ‘LOG’) |
index field |
- Primary key
job_type_id
- Index fields
job_id, type
This table stores job types given with the oarsub command and “-t” options.
resources
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
resource_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
resource identifier |
type |
VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT “default” |
resource type (used for licence resources for example) |
network_address |
VARCHAR(100) |
node name (used to connect via SSH) |
state |
ENUM(‘Alive’, ‘Dead’ , ‘Suspected’, ‘Absent’) |
resource state |
next_state |
ENUM(‘UnChanged’, ‘Alive’, ‘Dead’, ‘Absent’, ‘Suspected’) DEFAULT ‘UnChanged’ |
state for the resource to switch |
finaud_decision |
ENUM(‘YES’, ‘NO’) DEFAULT ‘NO’ |
tell if the actual state results in a “finaud” module decision |
next_finaud_decision |
ENUM(‘YES’, ‘NO’) DEFAULT ‘NO’ |
tell if the next node state results in a “finaud” module decision |
state_num |
INT |
corresponding state number (useful with the SQL “ORDER” query) |
suspended_jobs |
ENUM(‘YES’,’NO’) |
specify if there is at least one suspended job on the resource |
scheduler_priority |
INT UNSIGNED |
arbitrary number given by the system to select resources with more intelligence |
switch |
VARCHAR(50) |
name of the switch |
cpu |
INT UNSIGNED |
global cluster cpu number |
cpuset |
INT UNSIGNED |
field used with the JOB_RESOURCE_MANAGER_PROPERTY_DB_FIELD |
besteffort |
ENUM(‘YES’,’NO’) |
accept or not besteffort jobs |
deploy |
ENUM(‘YES’,’NO’) |
specify if the resource is deployable |
expiry_date |
INT UNSIGNED |
field used for the desktop computing feature |
desktop_computing |
ENUM(‘YES’,’NO’) |
tell if it is a desktop computing resource (with an agent) |
last_job_date |
INT UNSIGNED |
store the date when the resource was used for the last time |
available_upto |
INT UNSIGNED |
used with compute mode features to know if an Absent resource can be switch on |
- Primary key
resource_id
- Index fields
state, next_state, type, suspended_jobs
State explications:
“Alive” : the resource is ready to accept a job.
“Absent” : the oar administrator has decided to pull out the resource. This computer can come back.
“Suspected” : OAR system has detected a problem on this resource and so has suspected it (you can look in the event_logs table to know what has happened). This computer can come back (automatically if this is a “finaud” module decision).
“Dead” : The oar administrator considers that the resource will not come back and will be removed from the pool.
This table permits to specify different properties for each resources. These can be used with the oarsub command (“-p” and “-l” options).
You can add your own properties with oarproperty command.
These properties can be updated with the oarnodesetting command (“-p” option).
Several properties are added by default:
switch : you have to register the name of the switch where the node is plugged.
cpu : this is a unique name given to each cpus. This enables OAR scheduler to distinguish all cpus.
cpuset : this is the name of the cpu on the node. The Linux kernel sets this to an integer beginning at 0. This field is linked to the configuration tag JOB_RESOURCE_MANAGER_PROPERTY_DB_FIELD.
resource_logs
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
resource_log_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
unique id |
resource_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
resource identifier |
attribute |
VARCHAR(255) |
name of corresponding field in resources |
value |
VARCHAR(255) |
value of the field |
date_start |
INT UNSIGNED |
interval start date |
date_stop |
INT UNSIGNED |
interval stop date |
finaud_decision |
ENUM(‘YES’,’NO’) |
store if this is a system change or a human one |
- Primary key
None
- Index fields
resource_id, attribute
This table permits to keep a trace of every property changes (consequence of the oarnodesetting command with the “-p” option).
assigned_resources
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
moldable_job_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
job id |
resource_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
resource assigned to the job |
- Primary key
moldable_job_id, resource_id
- Index fields
moldable_job_id
This table keeps informations for jobs on which resources they were scheduled.
queues
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
queue_name |
VARCHAR(100) |
queue name |
priority |
INT UNSIGNED |
the scheduling priority |
scheduler_policy |
VARCHAR(100) |
path of the associated scheduler |
state |
ENUM(‘Active’, ‘notActive’) DEFAULT ‘Active’ |
permits to stop the scheduling for a queue |
- Primary key
queue_name
- Index fields
None
This table contains the schedulers executed by the oar_meta_scheduler module. Executables are launched one after one in the specified priority.
challenges
Fields |
Types |
Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
job_id |
INT UNSIGNED |
job identifier |
challenge |
VARCHAR(255) |
challenge string |
ssh_private_key |
TEXT DEFAULT NULL |
ssh private key given by the user (in grid usage it enables to connect onto all nodes of the job of all clusers with oarsh) |
ssh_public_key |
TEXT DEFAULT NULL |
ssh public key |
- Primary key
job_id
- Index fields
None
This table is used to share a secret between OAR server and oarexec process on computing nodes (avoid a job id being stolen/forged by malicious user).
For security reasons, this table must not be readable for a database account given to users who want to access OAR internal informations(like statistics).